What is the difference between barcoding and RFID?
In the world of data capture, barcoding has been a staple for a very long time, but over the last few years, RFID has made steady growth and is quickly becoming a preferred option for auto-ID solutions. So, what are the differences between the two? What are the pros and cons of each of these revolutionary technologies?
What is barcoding?
Barcoding is used to store information and identify things, particularly in warehouses or at other points in the supply chain. Barcodes can be used not only to store information about an item but also to help manage and track items. Like RFID, barcodes can be used for both inventory management and asset management.
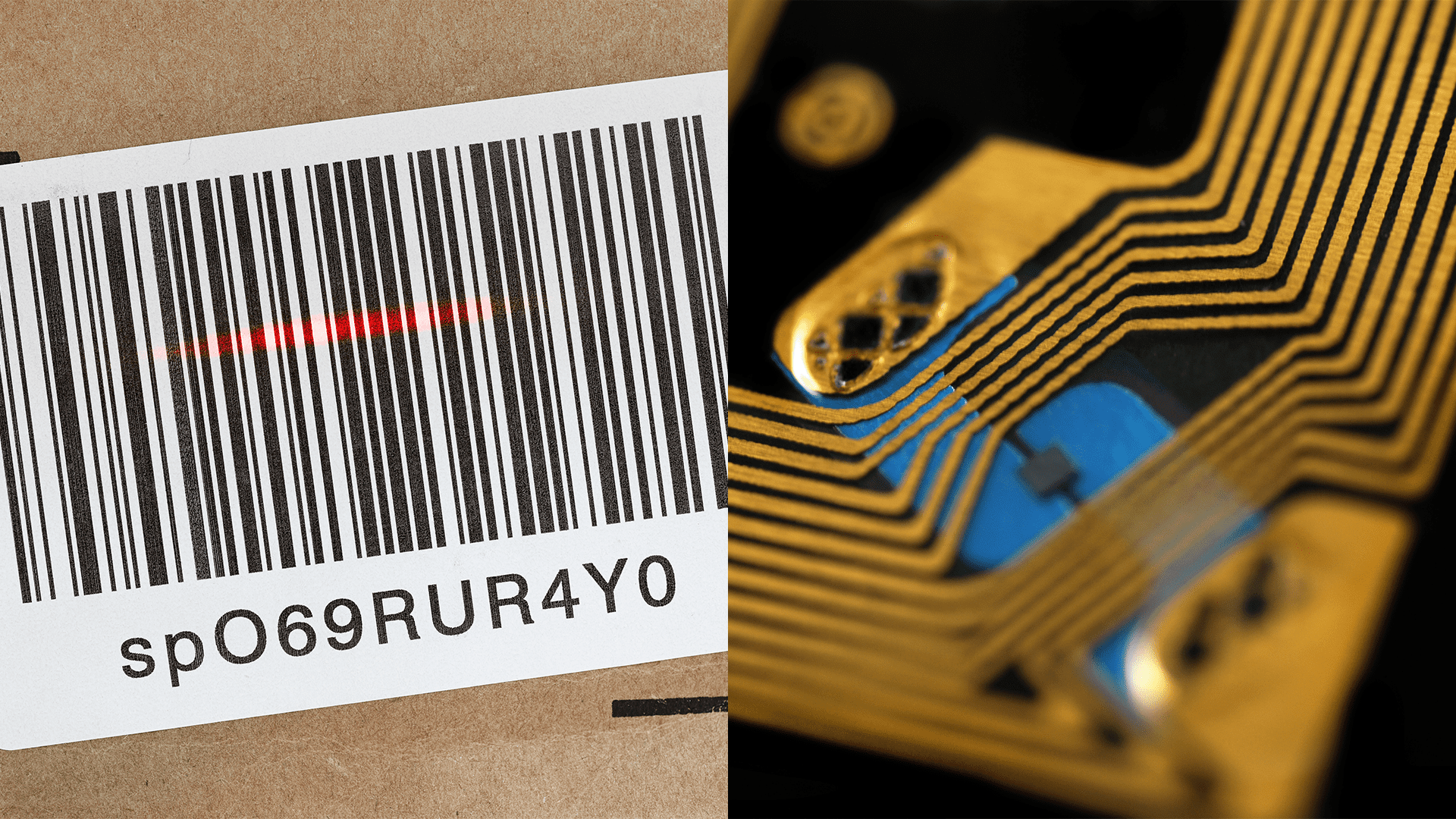
Barcodes work by using a barcode scanner and a barcode. Different barcodes have different formats, such as QR codes, but the ‘typical’ barcode has a series of lines in either white or black to allow the scanner to read it, such as the one below. This particular barcode is a universal product code, or UPC, which is typically used in grocery stores to allow for items to be quickly scanned and added to a customer’s receipt.
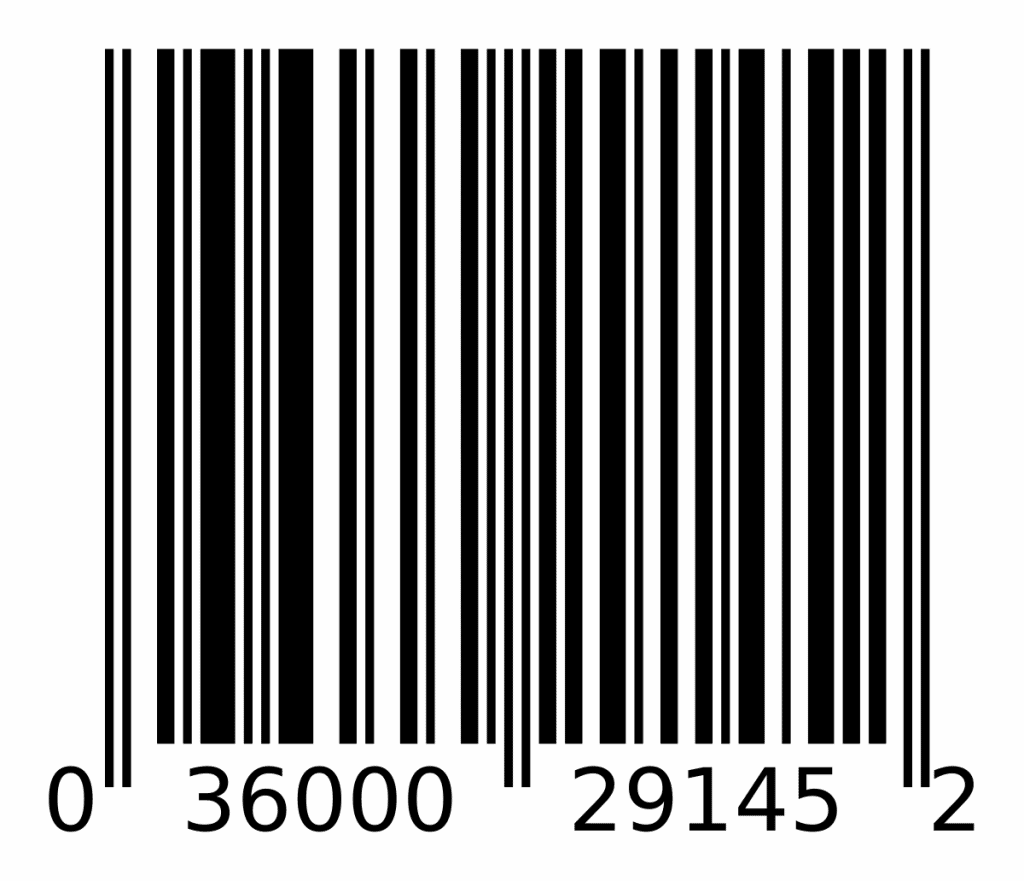

This type of barcode is known as a linear barcode, as the barcode is only read along one axis (horizontally), but there are other types of barcodes, known as 2d barcodes, that read both horizontally and vertically. These barcodes are able to store more data about an item but require scanners that are specifically capable of reading them in order to be read. A great example of a 2D barcode is a Quick Response code or QR code as they are more commonly known, such as the one below. QR codes can be used for many applications, as the 2D barcode allows for much more data to be stored. Often you will find businesses using QR codes to direct customers to a website or app, by scanning the QR code with their mobile phone – something that most modern mobile phones support.

What is RFID?
RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, is a technology that is also used to store data about tagged items, much like barcodes. RFID can be used for supply chain management like barcodes, but can also be used for many other things, such as contactless NFC payments. RFID has a very high read range, meaning that when it is used for supply chain applications, it is quick and easy to see information about many tagged items in a wide area.
RFID works by using RFID scanners and RFID tags, which have an RFID chip, antenna, and substrate. The RFID chip is where the data held in the tag is stored and can vary in size greatly depending on the tag. Some RFID chips can hold up to 2KB of data on them, which is significantly more than barcodes. The antenna makes up the majority of a tag and is used to receive and transmit signals from the reader. The antenna is what allows for the tag to communicate, and if the tag is an active tag, it will constantly transmit signals. Finally, the substrate is the material the tag is made out of. An advantage of RFID tags is that they can be created in many form factors, meaning they are versatile and can be adapted to their conditions, so the substrate could be anything from a paper label to a hard plastic key fob.


So what exactly is the difference?
Although both types of tag essentially do the same thing (store and transmit data) the way they do it is quite different. Barcodes can be scanned by visually reading the bars on the barcode using a barcode scanner, which then decodes the barcode and presents it in a readable format to the user. RFID however requires no line of sight between the tag and the reader, and instead the reader reads the tag by using signals transmitted by the reader to create a response from the tag (the response holding the tag’s data). The response is then detected and decoded by the reader into a format readable to the user of the reader.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of barcodes and RFID?
There are many advantages and disadvantages to both of these technologies. Below we have listed some of the key advantages and disadvantages of each of these technologies, that you should consider when implementing one of these solutions into your business.
Barcode Advantages
- Cheaper to buy and implement
- Can read barcodes regardless of what the barcode is on. RFID signals can be blocked by materials such as liquids and metal.
- Widely used and understood.
Disadvantages
- Easily damaged and obscured to the point they can no longer be read.
- Read-only functionality.
- Each barcode must be scanned individually, making them more time consuming to scan.
- Each barcode must be scanned with a direct line of sight, also making them more time consuming to scan.
- Cannot be used for many applications that RFID can, like animal tracking for example.
- Can hold significantly less data than an RFID tag can.
- Much shorter read range due to line of sight being a requirement.
- No serialisation so items cannot be uniquely identified.
RFID Advantages
- Can hold significantly more data than a barcode – typically between 64 and 1000 bits, but it can be more.
- Significantly greater read range than barcodes. Passive RFID tags have a read range typically between 1 and 25 metres, but active tags can be even further, usually between 30 and 300 metres!
- Many RFID tags can be scanned at once, reducing the time taken to scan.
- Line of sight is not needed to scan RFID tags.
- Tags can be designed to be highly durable making them suitable for use in harsh conditions.
- Can be used for many applications, as the tags’ substrate can be designed in many form factors, allowing for applications that can’t be achieved by barcodes.
- Read and write functionality (for active RFID tags).
- Can be used to uniquely identify each tagged item, allowing for more information to be held about a tagged item, such as the status of the item.
Disadvantages
- Some items cannot be read when tagged, such as liquids and metals.
- Much more expensive to implement, and slightly more expensive to use.
Which is right for me?
Ultimately, the option that’s right for you will depend greatly on what you need to tag. RFID is a better option for tracking high value assets and barcoding works well for tracking lower value assets and products. At TEC-RFID we offer barcode and RFID solutions, so get in touch with us and our team can assess your needs and recommend a data capture solution for your business.